Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is an important technology to reduce energy consumption in buildings by preventing heat gain/loss through the building envelope. These materials have no other purpose than to save energy and protect and provide comfort to occupants.



At Abu Anas LLC we have trained and certified installers of EIFS system involving a complete wrap of the building with insulation material and providing finish approved by the client as well as ceramic coating applicators for insulation of metal roofs, pipeline, steel structure and metal tanks.

External Insulation -EIFS
Carried out the application of EIFS [ External Insulation and Finish System ] at Mall of Oman which is an iconic project and the biggest mall in Oman by Majid Al Futaim.
According to the definitions of the International Building Code and ASTM International, an Exterior Insulation and Finish System (EIFS) is a nonload bearing, exterior wall cladding system that consists of an insulation board attached either adhesively or mechanically, or both, to the substrate; an integrally reinforced base coat; and a textured protective finish coat.
Top Advantages of EIFS System
The growing popularity of EIFS is since few, if any, competitive materials offer such a wide range of desirable product benefits. Chief among these are superior energy efficiency and virtually unlimited design flexibility.
Energy Efficiency and Energy Codes
EIFS can reduce air infiltration by as much as 55% compared to standard block work construction. And since walls are one of the greatest areas of heat and air conditioning loss, improvement in the wall insulation can be very meaningful in terms of energy conservation.
Another point to keep in mind on new construction: Due to the energy efficiency of EIFS, it may be possible to specify lower-capacity heating and air conditioning equipment without sacrificing anything in terms of interior comfort.
Durability
Unlike stucco, plaster, and other materials, EIFS rarely need painting. Most EIFS systems are specially formulated with 100% acrylic binder, which gives EIFS superior resistance to fading, chalking, and yellowing. As a result, the systems tend to maintain their original appearance over time. And since the colour is integral to the finish coat, even if the surface is scratched, the same colour appears beneath the abrasion.
The EIFS systems are designed to be very flexible, which makes them highly crack resistant. When walls expand or contract due to rising or falling temperatures, EIFS are resilient enough to “absorb” building movement and thus avoid the unsightly cracking problems that are so common with stucco, concrete and block exteriors.
Impact Resistance
EIFS are sustainable, durable, and resilient. Highly impact resistant EIFS are easily achievable using industry standard application practices and products that are very effective and economical. The keys to high impact resistant EIFS are the same as for any quality construction: good design, firm and definitive specifications, use of the proper products, and proper construction.

Design Flexibility/Aesthetics
The rich appearance of EIFS bears a resemblance to stucco or stone, but the systems are far more versatile than these and other materials. Not only do EIFS come in virtually limitless colours and a wide variety of textures, but they also can be fashioned into virtually any shape or design.
With EIFS, skilled applicators can create all sorts of exterior architectural detailing that would often be cost-prohibitive using conventional construction — cornices, arches, columns, keystones, cornerstones, etc.
Moisture Control
EIFS are among the most water resistant exterior surfaces you can put on a house. But as with all claddings, EIFS must be correctly installed and properly detailed if they are to perform properly.
Fire Testing
EIFS have passed the major fire resistance tests that are required by the building codes. EIFS have passed fire resistance, ignitability, intermediate multi-story, and full scale multi-story corner tests; meeting the standards set forth with each test.






Ceramic Thermal Insulation
A Ceramic coating is a paint mixed with one or more ceramic compounds for application via spray or roller to exterior and interior surfaces. Depending on the ceramic compounds used, this insulating product has the ability to prevent heat transfer and heat loading onto a structure. This means heat will not transfer into or out of a building.
Liquid nano-ceramic thermal insulation coatings appeared in the last decades on the market of thermal insulation materials. This paint-on insulation contains microscopic cellular ceramic microspheres. These vacuum-hollow balls were made of on high temperature melted ceramic. Its binding material is a mixture of synthetic rubber and other polymers. After mixing with the raw material with its binder, using brush or vacuum vaporizer can be taken on the surface to be insulated. The ceramic spheres, the principle component of the Ceramic product reduces heat transfer using a very thin coating beyond most common insulations in today’s market.

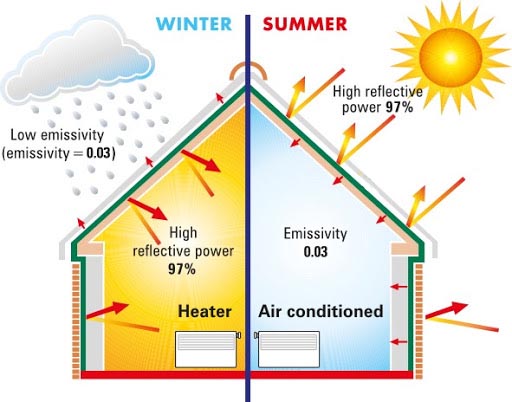
A ceramic coating is a paint mixed with one or more ceramic compounds for application via spray or roller to exterior and interior surfaces. Depending on the ceramic compounds used, this insulating product has the ability to prevent heat transfer and heat loading onto a structure. This means heat will not transfer into or out of a building. Ceramic coating has been around for almost 20 years and is highly effective in preventing unnecessary heat loss or gain in residential and commercial structures. This technology far surpasses the ability of older, obsolete coating products. Ceramic coating can save as much as 40% of the energy cost for cooling / heating of residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
Ceramic Insulation coatings effectiveness is based on resisting all three types of heat transfer.
1
Conventional heat transfer
Convention is transfer of heat through a liquid or gas caused by molecular motion. Ceramic insulation coatings high resistance to air circulation’s convectional cooling effect is specially valuable for warming cold surfaces and preventing condensation which leads to rust and corrosion.
2
Conduction heat transfer
Conduction is the transfer of heat between substances that are in direct contact with each other. The better the conductor, the more rapidly heat will be transferred. Metal is a good conduction of heat. Conduction occurs when a substance is heated, particles will gain more energy, and vibrate more. These molecules then bump into nearby particles and transfer some of their energy to them. This then continues and passes the energy from the hot end down to the colder end of the substance.
3
Radiation heat transfer
Radiation is a method of heat transfer that does not rely upon any contact between the heat source and the heated object as in the case with convection and conduction. Heat can be transmitted through empty space by thermal radiation often called infra radiation. This is a type of electromagnetic radiation. No mass is exchanges or no medium is exchanged, and no medium is required in the process of radiation. Example of radiation is the heat from the sun, or heat released from the filament of a light bulb.

Ceramic insulation Vs traditional facade insulation
Unlike fiberglass insulation, whose R-value rating assumes heat loading by a building and simply measures the rate at which that heat is transferred, ceramic coatings are not given an R-value rating. Instead, they are rated by “emissivity” a measure of both their ability to reflect heat and the amount of heat that is loaded onto a surface.
“The true key to insulation is preventing heat load”. The concept is simple: Why use fiberglass insulation to slow the transfer of heat into a building when you can just prevent that heat from ever loading onto the building in the first place? If heat is kept off the structure to begin with, that fiberglass insulation becomes unnecessary. It’s a change in the way we think about insulating our homes against energy lost.
Thermal insulation & protection for industrial use.
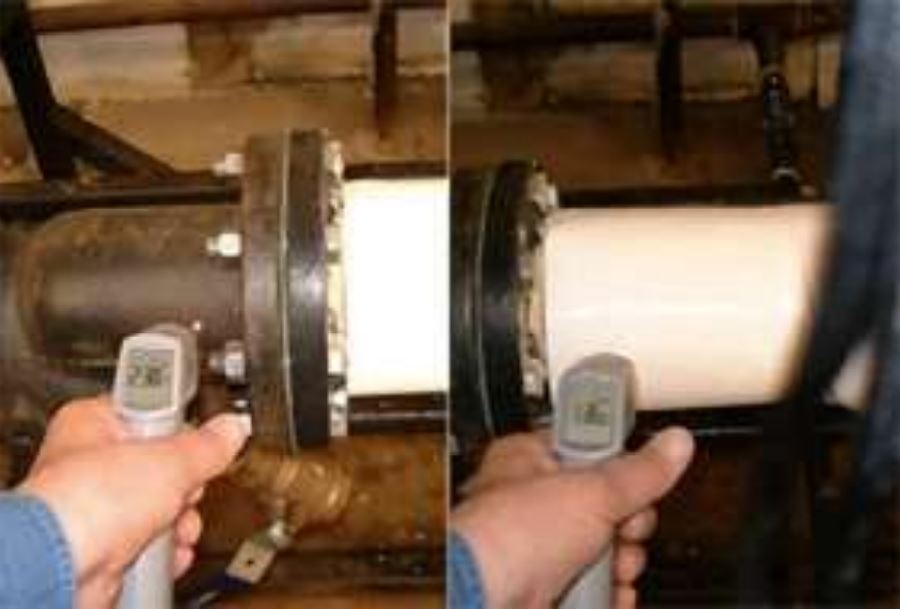
Systems with piping and tanks constantly exposed to the weathering, sunlight and UV rays face continuous maintenance on insulation. With the use of ceramic coating the problem has been resolved along with a reduction in energy consumption and a decrease in operation temperature.
Ceramic coating keeps heat in the pipes / tanks and therefore there is a significant reduction in the amount of energy needed to heat the steam leading to considerable energy saving.
Steam pipes at a temperature of 187 degree Celsius, after applying a thin coat at a thickness of 1 mm the temperature were reduced to 118 degree Celsius.













